- Overview
- Applications
- Benefit
- Spesification
Overview
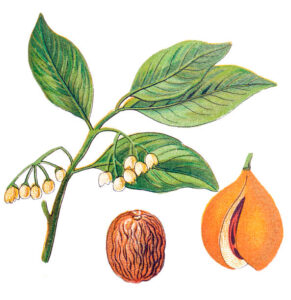
Nutmeg has the Latin name Myristica fragrans. It is also known by other common names such as mace, muscdier, magic, muskatbaum, noz moscada, myristica, nuez moscada and nux moschata.
The story of this spice originally grown in the Moluccas (also called the Spice Islands) is inevitably linked to the games of power among several countries in a time where spices where precious trading items.
Before the 15th century the Arabs had control over nutmeg’s export transactions to Europe, but in 1512 Portugal claimed the islands and established the nutmeg monopoly. Later, in 1602, the Dutch took over the territory and worked their way to preserve the spice’s domain. Some sources say in case of abundant harvest they would even burn nutmeg to keep its supply under control. Despite the safety measures, the French found the way to smuggle some seeds, then the English occupied the Moluccas and extend nutmeg cultivation to some of their colonies in East India and the Caribbean.
While ambitious merchants were quarrelling over its possession, nutmeg became very popular among wealthy people of different nationalities. Some used them as amulets, others to attract admirers and some more because of its alleged aphrodisiac powers.
Nutmeg has been used for centuries, particularly as a remedy for kidney and digestive problems; Nutmeg oil is obtained from an evergreen tree of the Myristicaeae plant family. The tree grows up to sixty five feet in height with small, yellow flowers and fruit, shaped like a small peach; the bark of the tree is smooth and gray-brown in color. It is native to the Molucca Islands and cultivated in the West Indies, Indonesia and Sri Lanka.
Nutmeg Use Through History
Ancient Indian and Chinese royalty carried ground Nutmeg in small, ivory boxes and added the substance to drinks for hallucinogenic reasons; in Malaysia, pregnant women used Nutmeg in the final weeks of their confinement in the belief it would strengthen the uterine muscle for labor. The Romans used Nutmeg to make incense.
Nutmeg was considered to be a valuable spice for trading; both the British and the French smuggled Nutmeg seeds in the eighteenth century. By the nineteenth century, ground Nutmeg was being used in many English recipes; it became a popular addition to Christmas eggnog in the Uni

Application
Nutmeg Oil has been widely applied in industry and pharmaceuticals clams as a main ingredient or supporting materials produced products industry. Nutmeg oil contained in various kinds of products such as spices, food & beverages, fragrances, health and others.
Nutmeg oil has a warm, spicy, sharp aroma; it has a number of properties including being analgesic, anti-septic, digestive, an aphrodisiac, stimulant, tonic and anti-oxidant. In aromatherapy, Nutmeg is used in the treatment of a number of conditions; it is used to treat arthritis, gout, rheumatism, poor circulation, indigestion, constipation, flatulence, nausea, nervous fatigue and anxiety.
Nutmeg is also used as a flavoring agent in pharmaceuticals; it is used in soaps, cosmetics, perfumes, detergents and lotions. Mace oil is also used interchangeably with Nutmeg and is found in many colognes and perfumes, particularly fragrances for men; Mace is also found in many foods and drinks, both alcoholic and non-alcoholic.
Food and Beverages
Application Nutmeg is used in a variety of cuisines, and the essential oil of the seed has medicinal applications. In India, nutmeg is commonly used in sweet dishes, but also in a mixture of spices called garam masala. Nutmeg is also an ingredient in Japanese curries. In Western Europe, nutmeg more often appears in savory dishes, including cheese sauces, soups, and potato and meat dishes. Mulled wine or cider also commonly includes nutmeg, along with other spices.
Oil of nutmeg is also used as a flavoring in some products, particularly when the grains of ground nutmeg would be undesirable, as in Coca-Cola and toothpaste. The oil also has some therapeutic uses. Like oil of clove, it can be used topically to treat the pain of arthritis or toothache. It can also be taken with a small amount of sugar or honey to sooth gastrointestinal complaints. When diluted in almond oil, it makes an excellent massage oil for sore muscles or for the abdomen of a pregnant woman. Another nutmeg product is nutmeg butter, which can be substituted for cocoa butter or used as an industrial lubricant.
Another popular uses is fragrance. Nutmeg oil as fragrans can be found among big name such as Chanel, Giorgio, Dior, Calvin Klein and another famous name in the world of fragrans.
General Uses
The essential oil is obtained by the steam distillation of ground nutmeg and is used heavily in the perfumery and pharmaceutical industries. The oil is colorless or light yellow and smells and tastes of nutmeg. It contains numerous components of interest to the oleochemical industry, and is used as a natural food flavouring in baked goods, syrups (e.g. Coca Cola), beverages, sweets etc. It replaces ground nutmeg as it leaves no particles in the food. The essential oil is also used in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries for instance in tooth paste and as a major ingredient in some cough syrups. In traditional medicine nutmeg and nutmeg oil were used for illnesses related to the nervous and digestive systems. Myristicin in the essential oil is probably the agent responsible for the hallucinogenic properties of nutmeg oil.
External Uses
Externally, the oil is used for rheumatic pain and, like clove oil, can be applied as an emergency treatment to dull toothache. In France, it is given in drop doses in honey for digestive upsets and used for bad breath. Some recommend using 1-2 drops on a cotton swab, and apply to the gums around an aching tooth until dental treatment can be obtained; or 3-5 drops on a sugar lump or in a teaspoon of honey for nausea, gastroenteritis, chronic diarrhea, and indigestion.
Alternatively a massage oil can be created for muscular pains associated with rheumatism or overexertion. It can also be combined with thyme or rosemary essential oils.


Benefit
The health benefits of nutmeg oil include its ability to treat stress, pain, menstrual cramps, heart disorders, indigestion, blood pressure, cough and bad breadth. The health benefits of nutmeg oil can be attributed to its medicinal properties such as sedative, stimulant, relaxing, anti inflammatory, antiseptic, bactericide, etc.
The health benefits of nutmeg oil include the following:
Pain Relief: Nutmeg oil is very useful for treating muscular and joint pain and sores as it is an excellent sedative. Nutmeg oil is also anti-inflammatory and therefore massaging the part that is in pain with nutmeg oil is an effective treatment for arthritis, rheumatism, lumbago, etc. Nutmeg oil is an essential part of the Chinese medicine when it comes to treating abdominal pain, and inflammation. It reduces the swelling of joints. Often, overexertion leads to body or muscle ache. In such cases nutmeg oil can be very useful to remove the pain.
Menstrual Cramps: Some women often face menstrual irregularities and have menstrual cramps. Nutmeg oil is very helpful for these people.
Indigestion: Nutmeg oil is good for digestion and helps in removing stomach aches and removing gas from stomach and intestine. Therefore, nutmeg oil is good for indigestion, flatulence, vomiting, diarrhea, etc. It also encourages appetite. Care should be taken to consume nutmeg oil internally in lower doses.
Respiratory Problems: Nutmeg oil form an important ingredient in many cough syrups and cold rubs as it helps in relieving cough and cold. It is also believed that nutmeg oil can be used for treating asthma.
Blood Pressure: Nutmeg oil is a good stimulant not just for the mind but also for the entire body. Its relaxing aroma comforts the body, increases blood circulation and therefore helps those who have poor blood circulation.
Respiratory Problems: Nutmeg oil form an important ingredient in many cough syrups and cold rubs as it helps in relieving cough and cold. It is also believed that nutmeg oil can be used for treating asthma.
Brain Tonic: Nutmeg oil stimulates the brain and therefore removes mental exhaustion and stress. It is also believed that nutmeg oil improves the quality of your dreams, making them more intense and colorful. It is a good remedy for anxiety as well as depression. Nutmeg oil is often used in homeopathy. In the ancient Greek and Roman civilizations, nutmeg was popular as an effective brain tonic in spite of its high cost and rarity. Nutmeg oil also enhances concentration and increases your overall efficiency at study and work.
Heart Problems: Nutmeg oil also stimulates the cardiovascular system and therefore is a good tonic for the heart.
Bad Breath: The woody aroma of nutmeg oil helps in removing bad breadth. It is also antiseptic in nature and is effective for toothaches and aching gums. As a result, it is also added in numerous toothpastes.
Liver Tonic: An important health benefit of nutmeg oil is its ability to treat liver diseases. The oil is capable of removing toxins from the liver, thereby making it a good liver tonic.
Kidney: Nutmeg oil is often recommended for treating kidney infections and kidney diseases. It also helps in dissolving kidney stones.


Spesifications
Hazards Identification
- Potential Acute Health Effects: Hazardous in case of ingestion. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of inhalation.
- Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available.
- TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available.
- DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. Repeated or prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition.
First Aid Measures
- Eye Contact: No known effect on eye contact, rinse with water for a few minutes.
- Skin Contact: After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water. Gently and thoroughly wash the contaminated skin with running water and non-abrasive soap. Be particularly careful to clean folds, crevices, creases and groin. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. If irritation persists, seek medical attention. Wash contaminated clothing before reusing.
- Serious Skin Contact: Not available.
- Inhalation: Allow the victim to rest in a well ventilated area. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Serious Inhalation: Evacuate the victim to a safe area as soon as possible. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Seek medical attention.
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Serious Ingestion: Not available.
Fire and Explosion Data
- Flammability of the Product: Flammable.
- Auto-Ignition Temperature: Not available.
- Flash Points: CLOSED CUP: 43°C (109.4°F).
- Flammable Limits: Not available.
- Products of Combustion: Not available.
- Fire Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Not available.
- Explosion Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not available. Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available.
- Fire Fighting Media and Instructions: Flammable liquid, insoluble in water.
- SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder.
- LARGE FIRE: Use water spray or fog. Cool containing vessels with water jet in order to prevent pressure build-up, autoignition or explosion.
- Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Not available.
- Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Not available.
Accidental Release Measures
- Small Spill: Absorb with an inert material and put the spilled material in an appropriate waste disposal.
- Large Spill: Flammable liquid, insoluble in water. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Stop leak if without risk. Absorb with DRY earth, sand or other non-combustible material. Do not get water inside container. Do not touch spilled material. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or confined areas; dike if needed. Eliminate all ignition sources. Call for assistance on disposal.
Handling and Storage
- Precautions: Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Ground all equipment containing material. Do not breathe gas/fumes/ vapour/spray.
- Storage: Flammable materials should be stored in a separate safety storage cabinet or room. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Keep container tightly closed. Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place. Ground all equipment containing material. Keep container dry. Keep in a cool place.
Exposure Controls / Personal Protection
- Engineering Controls: Provide exhaust ventilation or other engineering controls to keep the airborne concentrations of vapors below their respective threshold limit value. Ensure that eyewash stations and safety showers are proximal to the work-station location.
- Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat.
- Personal Protection in Case of a Large Spill: Splash goggles. Full suit. Boots. Gloves. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product.
- Exposure Limits: Not available.